Geotargeting vs Geofencing: The Key Differences Retailers Should Know
 Devon Mastromarino
·
3 minute read
Devon Mastromarino
·
3 minute read
Have you ever wondered why you see ads for businesses near you when you're out and about? Location-based marketing is becoming increasingly popular, and for good reason - leveraging location to connect with customers can provide major benefits.
In this post, we’ll explore the power of location-based marketing and clarify the difference between two key tactics: geotargeting and geofencing.
With consumers constantly on mobile devices, location data provides valuable insight into their habits and movements. Strategic use of this data enables more relevant, timely outreach. Both methods provide key benefits for companies, especially manufacturers who sell through large dealer and retailer networks. For manufacturers, location-based marketing can increase engagement with local dealers and raise awareness of new products and promotions. For dealer network owners, it supports connecting with customers when they are nearby and most receptive to visiting your stores.
What is Geotargeting?
Geotargeting is a digital marketing technique that allows businesses to target their ads and content based on the geographic location of users. With geotargeting, businesses can focus their marketing efforts on specific regions, cities, zip codes, or neighborhoods. It works by using information such as GPS location and zip code to determine these locations. This allows marketers to serve localized ads and content to users based on their geographic region
For example, if you search for a hardware store, your search results will be based on your location. Most likely you will see a sponsored ad as your first result and because you are looking for a hardware store near you, this ad will most likely be successful. Here is an example of how that search result may look:
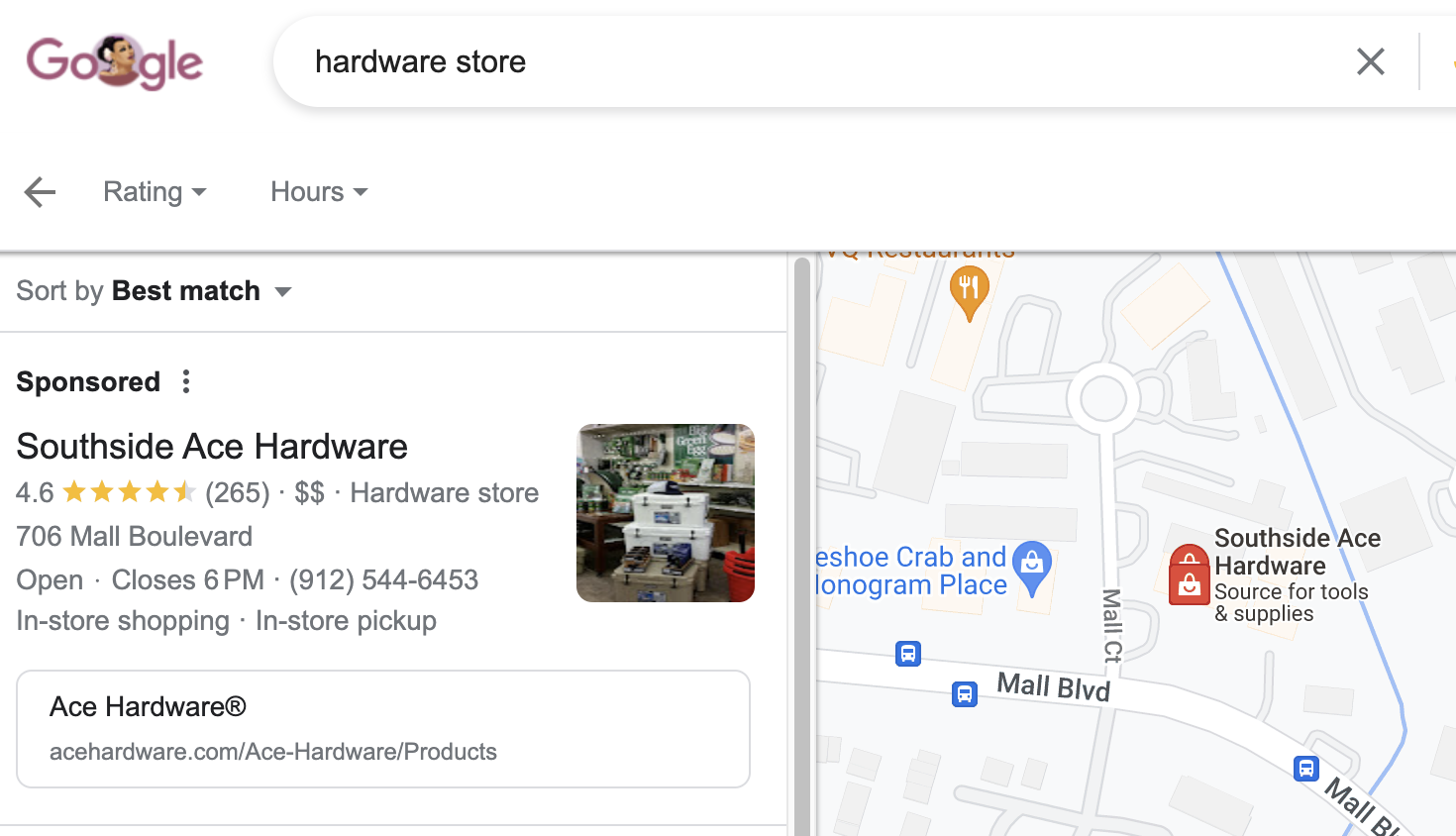
Overall, geotargeting gives businesses the ability to adjust their online marketing to be more relevant on a geographic basis. This can help increase engagement and conversions from localized audiences.
What is Geofencing?
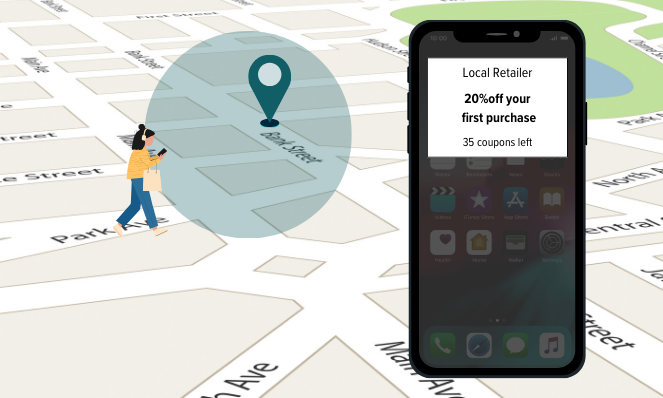
Geofencing is a location-based marketing tactic that allows companies to create virtual boundaries around specific geographic areas like stores, events, or neighborhoods. When a consumer enters or exits one of these designated zones with a mobile device, geofencing technology can trigger various actions like sending targeted messages, offering discounts, collecting data, and more. The goal is to engage with users based on their physical location
Geofencing relies on technologies like GPS, RFID, WiFi, and cellular data to accurately detect when a mobile device crosses into or out of a defined area. The virtual perimeters can be as large or small as a business wants, ranging from an entire city to specific aisles in a store. This allows for very precise and personalized marketing efforts.
As an example, imagine a coffee shop utilizing geofencing to establish a virtual boundary just 10 feet from their entrance. When a customer approaches this area, a notification could be seamlessly delivered to their mobile device offering a special discount. Perhaps the customer hadn't even considered grabbing a coffee, but this timely incentive might just be the nudge they need to step inside and make a purchase.
Key Differences
Geotargeting and geofencing are similar in that they both utilize location data, but they have some key differences in how they function.
Geotargeting involves targeting ads based on a user's general location. Geofencing involves creating triggers and actions when users enter or leave a precise geographic boundary. The main difference is that geotargeting casts a wide net based on location, while geofencing creates a virtual fence to target customers within a precise area.

When to Use Each
Keep in mind that both geofencing and geotargeting can complement each other in certain scenarios, and the choice between them depends on the specific goals of a campaign or application. So when is it best to use one versus the other? Here are some key differences in how they are best utilized:
-
Use geotargeting for regional ad campaigns. Geotargeting allows you to broadly target users within a city, state, or other geographic region. This makes it ideal for campaigns with a more general regional focus. For example, a retailer expanding to a new market could geotarget ads to everyone within that metro area.
-
Use geofencing to engage customers near stores. In contrast, geofencing allows for targeting users when they enter or exit a specific geographic area. This makes geofencing better suited for location-based campaigns focused on driving foot traffic to physical stores. For instance, a retailer could send push notifications to customers who enter the parking lot of a store.
-
Combine for targeted ads around key locations. Using geotargeting and geofencing together provides the ability to serve highly targeted ads to users both regionally and when they are near key locations. A retailer could geotarget ads across a metro area while also geofencing stores to engage customers who are nearby.
Used together, geotargeting and geofencing enable manufacturers to promote products, services, and offers to customers where and when they are most receptive. This can increase foot traffic to local dealers, boost engagement, and improve sales.
Drive the Right Customers to Your Products and Services.
Increase engagement and interest with location-based marketing today!

